第 7 章 分布检验
7.1 Q-Q图
x=read.table("data/ind.txt")
x=x$V1
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
qqplot(qnorm(((1:length(x))-0.5)/20,15,0.04),x)
z=(x-mean(x))/sd(x)
qqnorm(z);qqline(z)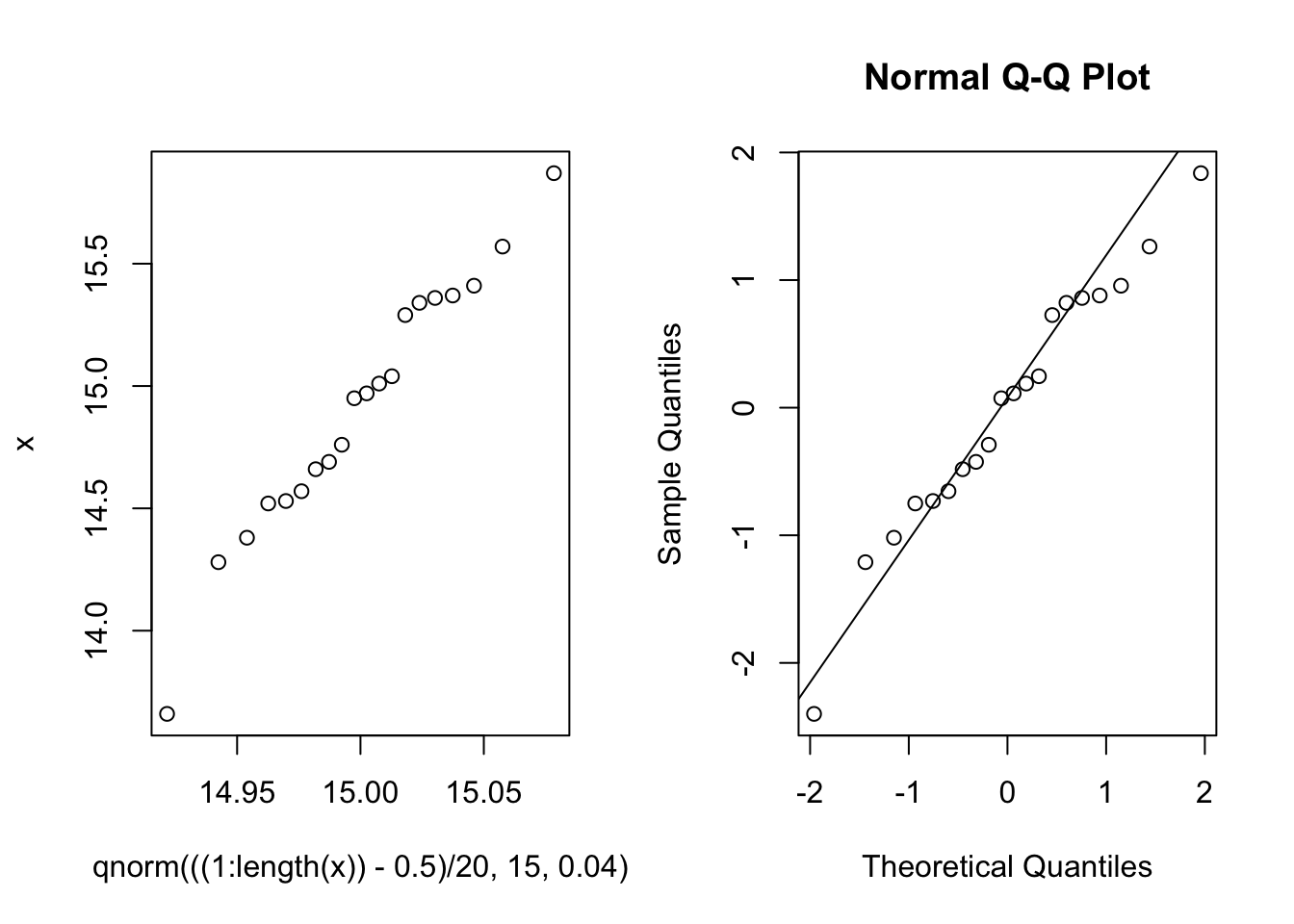
7.2 7.1 Kolmogorov-Smirnov单样本检验
7.2.1 KS检验
ks.test(x,"pnorm",15,0.2)##
## One-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test
##
## data: x
## D = 0.33943, p-value = 0.0147
## alternative hypothesis: two-sided7.2.2 正态性检验
shapiro.test(x)##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: x
## W = 0.97442, p-value = 0.8439library(nortest)
lillie.test(x)##
## Lilliefors (Kolmogorov-Smirnov) normality test
##
## data: x
## D = 0.11599, p-value = 0.6847ad.test(x)##
## Anderson-Darling normality test
##
## data: x
## A = 0.24208, p-value = 0.7364cvm.test(x)##
## Cramer-von Mises normality test
##
## data: x
## W = 0.03417, p-value = 0.7708pearson.test(x)##
## Pearson chi-square normality test
##
## data: x
## P = 3.1, p-value = 0.5412sf.test(x)##
## Shapiro-Francia normality test
##
## data: x
## W = 0.9683, p-value = 0.6274library(fBasics)## Loading required package: timeDate## Loading required package: timeSeriesnormalTest(x)##
## Title:
## Shapiro - Wilk Normality Test
##
## Test Results:
## STATISTIC:
## W: 0.9744
## P VALUE:
## 0.8439
##
## Description:
## Wed Aug 3 23:44:24 2022 by user:ksnormTest(x)##
## Title:
## One-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test
##
## Test Results:
## STATISTIC:
## D: 1
## P VALUE:
## Alternative Two-Sided: < 2.2e-16
## Alternative Less: < 2.2e-16
## Alternative Greater: 1
##
## Description:
## Wed Aug 3 23:44:24 2022 by user:shapiroTest(x)##
## Title:
## Shapiro - Wilk Normality Test
##
## Test Results:
## STATISTIC:
## W: 0.9744
## P VALUE:
## 0.8439
##
## Description:
## Wed Aug 3 23:44:24 2022 by user:jarqueberaTest(x)##
## Title:
## Jarque - Bera Normalality Test
##
## Test Results:
## STATISTIC:
## X-squared: 0.4222
## P VALUE:
## Asymptotic p Value: 0.8097
##
## Description:
## Wed Aug 3 23:44:24 2022 by user:dagoTest(x)##
## Title:
## D'Agostino Normality Test
##
## Test Results:
## STATISTIC:
## Chi2 | Omnibus: 0.9747
## Z3 | Skewness: -0.79
## Z4 | Kurtosis: 0.5922
## P VALUE:
## Omnibus Test: 0.6142
## Skewness Test: 0.4295
## Kurtosis Test: 0.5537
##
## Description:
## Wed Aug 3 23:44:24 2022 by user:7.3 7.2 Kolmogorov-Smirnov两样本分布检验
z=read.table("data/ks2.txt",header=F);
(x=z[z[,2]==1,1]);(y=z[z[,2]==2,1])## [1] 5.38 4.38 9.33 3.66 3.72 1.66 0.23 0.08 2.36 1.71 2.01 0.90 1.54## [1] 6.67 16.21 11.93 9.85 10.43 13.54 2.40 12.89 9.30 11.92 5.74 14.45
## [13] 1.99 9.14 2.89ks.test(x,y)##
## Two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test
##
## data: x and y
## D = 0.72308, p-value = 0.0004714
## alternative hypothesis: two-sided拟合优度\(\chi^2\)检验
7.4 7.3 Pearson \(\chi^2\) 拟合优度检验
Ob=c(490,334,68,16);n=sum(Ob);
lambda=c(t(0:3)%*%Ob/n)
p=exp(-lambda)*lambda^(0:3)/factorial(0:3)
E=p*n;
Q=sum((E-Ob)^2/E);
pvalue=pchisq(Q,2,low=F)7.4.1 Goodness-of-Fit Tests for a Single Discrete Random Variable
#Suppose we roll a die n = 370 times
#and we observe the frequencies (58, 55, 62, 68, 66, 61).
#Suppose we are interested in testing to see if the die is fair;
#i.e., p(j) ≡ 1/6.
x <- c(58,55,62,68,66,61)
chifit <- chisq.test(x)
chifit##
## Chi-squared test for given probabilities
##
## data: x
## X-squared = 1.9027, df = 5, p-value = 0.8624round(chifit$expected,digits=4)## [1] 61.6667 61.6667 61.6667 61.6667 61.6667 61.6667round((chifit$residuals)^2,digits=4)## [1] 0.2180 0.7207 0.0018 0.6505 0.3045 0.0072#(Birth Rate of Males to Swedish Ministers).
#This data is discussed on page 266 of Daniel (1978).
#It concerns the number of males in the first seven children
#for n = 1334 Swedish ministers of religion.
oc<-c(6,57,206,362,365,256,69,13)
n<-sum(oc)
range<-0:7
phat<-sum(range*oc)/(n*7)
pmf<-dbinom(range,7,phat)
rbind(range,round(pmf,3))## [,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5] [,6] [,7] [,8]
## range 0.000 1.000 2.00 3.000 4.00 5.000 6.000 7.000
## 0.006 0.047 0.15 0.265 0.28 0.178 0.063 0.009test.result<-chisq.test(oc,p=pmf)
pchisq(test.result$statistic,df=6,lower.tail=FALSE)## X-squared
## 0.4257546round(test.result$expected,1)## [1] 8.5 63.2 200.6 353.7 374.1 237.4 83.7 12.67.4.2 Several Discrete Random Variables
#(Type of Crime and Alcoholic Status).
#The contingency table, Table 2.1,
#contains the frequencies of criminals who committed certain crimes and whether or not they are alcoholics.
#We are interested in seeing whether or not the distribution of alcoholic status is the same for each type of crime.
#The data were obtained from Kendall and Stuart (1979).
c1 <- c(50,88,155,379,18,63)
c2 <- c(43,62,110,300,14,144)
ct <- cbind(c1,c2)
chifit <- chisq.test(ct)
chifit##
## Pearson's Chi-squared test
##
## data: ct
## X-squared = 49.731, df = 5, p-value = 1.573e-09(chifit$residuals)^2 #residuals=(observed - expected) / sqrt(expected)## c1 c2
## [1,] 0.01617684 0.01809979
## [2,] 0.97600214 1.09202023
## [3,] 1.62222220 1.81505693
## [4,] 1.16680759 1.30550686
## [5,] 0.07191850 0.08046750
## [6,] 19.61720859 21.94912045ct2 <- ct[-6,]
chisq.test(ct2)##
## Pearson's Chi-squared test
##
## data: ct2
## X-squared = 1.1219, df = 4, p-value = 0.8908